Abrir
Categorias
Postagens recentes
Na hora de escolher a fralda certa para o seu bebê, entender sua estrutura pode ser decisivo. Uma fralda não é apenas um simples pedaço de material absorvente; é um produto cuidadosamente projetado para manter seu bebê seco, confortável e sem assaduras. Vamos dar uma olhada mais de perto nos principais componentes que compõem uma fralda típica.
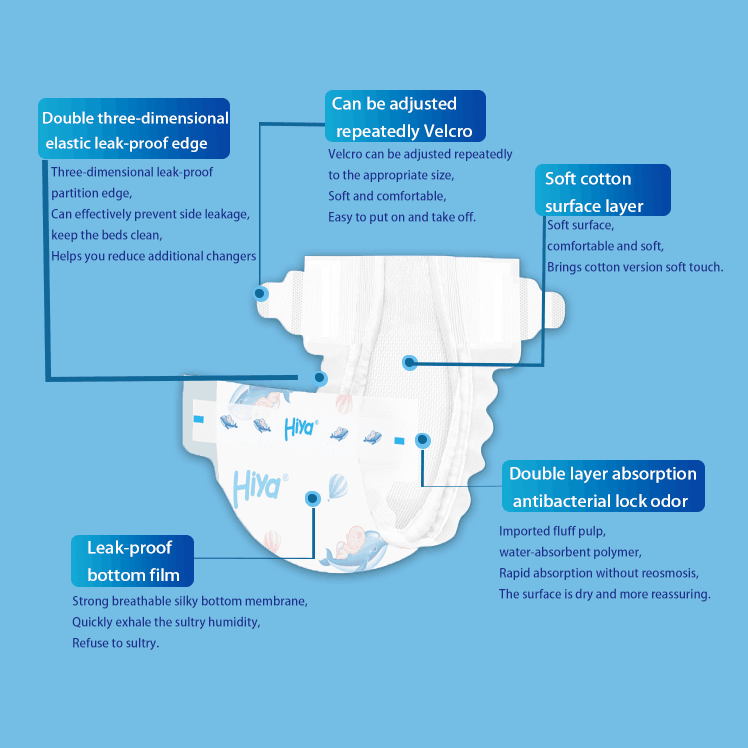
Função: Sua principal função é transferir rapidamente a urina para longe da pele do bebê. O tecido não tecido permite rápida absorção, evitando que a pele fique em contato prolongado com a umidade. Isso é crucial para reduzir o risco de assaduras. Algumas fraldas de alta qualidade possuem até um recurso adicional nessa camada, como um indicador de umidade. Trata-se de uma pequena faixa, geralmente amarela, que muda para azul ou verde quando a fralda está molhada. Ela proporciona uma maneira conveniente para os pais saberem quando é hora de trocar a fralda, especialmente durante a noite ou quando o bebê ainda não consegue se comunicar.
Função: Esta camada é responsável por capturar, armazenar e reter a urina. Assim que a urina passa pela camada interna, a polpa felpuda inicialmente a espalha. Em seguida, o SAP entra em ação, absorvendo rapidamente o líquido e transformando-o em uma substância gelatinosa. Isso não só evita vazamentos, como também garante que a superfície da fralda permaneça seca ao toque. A qualidade e a quantidade dos materiais do núcleo absorvente impactam diretamente no desempenho geral da fralda. Por exemplo, uma fralda com maior proporção de SAP de alta qualidade terá melhor absorção e poderá durar mais entre as trocas.
Função: Esta camada, também conhecida como "camada de aquisição" ou "camada de distribuição", ajuda a distribuir uniformemente a urina pelo núcleo absorvente. Ela garante que o núcleo absorvente seja utilizado de forma eficiente, evitando a formação de pontos úmidos concentrados. Ao distribuir o líquido uniformemente, a fralda mantém sua integridade e absorção por mais tempo. Isso é particularmente importante para bebês ativos, pois seus movimentos podem causar acúmulo de urina em certas áreas. A camada de distribuição ajuda a neutralizar isso, garantindo que a fralda permaneça eficaz ao longo do dia.
Função: A principal função da camada externa é evitar qualquer vazamento de urina ou fezes da fralda. A película de PE à prova d'água atua como uma barreira, mantendo o líquido dentro da fralda. Ao mesmo tempo, o tecido não tecido na superfície externa garante que a fralda não seja apenas à prova de vazamentos, mas também confortável de usar. Ele evita que a fralda fique plástica ou cause irritação na pele do bebê através das roupas. Além disso, algumas fraldas possuem elásticos nas pernas e cós. Estes são feitos de materiais elásticos e são uma parte importante da camada externa. Os elásticos nas pernas, frequentemente chamados de "protetores contra vazamentos", se ajustam perfeitamente às coxas do bebê, evitando qualquer vazamento lateral. O cós elástico proporciona um ajuste seguro e confortável ao redor da cintura do bebê, permitindo movimentos enquanto mantém a integridade da fralda.
Função: O sistema de fecho é crucial para garantir que a fralda permaneça no lugar no bebê. As abas adesivas ou fechos de velcro permitem um ajuste fácil do aperto da fralda. Isso é importante, pois os bebês vêm em tamanhos e formas diferentes, e seus tamanhos mudam rapidamente. O sistema de fecho deve ser forte o suficiente para manter a fralda segura durante os movimentos do bebê, seja engatinhando, andando ou apenas se contorcendo. Ao mesmo tempo, deve ser fácil de abrir e fechar, especialmente durante as trocas de fralda. Algumas fraldas têm até vários pontos de ajuste nas abas, permitindo um ajuste mais personalizado.
 fjxingyuan
fjxingyuan
 Linda@fjxingyuangroup.com
Linda@fjxingyuangroup.com
 360391852
360391852
 +86-595-85922600
+86-595-85922600
 +86-13514004600
+86-13514004600
 Escaneie nosso WeChat
Escaneie nosso WeChat

